How Online Communication will Evolve in the Post-COVID-19 Era
Technologies Driving the Online Communication Evolution
1.Outline of Technologies
The COVID-19 pandemic required social distancing and thus accelerated the spread of online communication overnight. Online communication connects people through networks using images and sounds converted to digital data. Online communication can range from one-to-one dialogue to multi-person meetings and seminars. ICT enables online communication through its specific technologies that connect people via networks, transmit information, and digitize and convey images and sounds. Once converted to digital data, audio and video can be processed and analyzed in a host of ways. With the introduction of new technologies, online communication based on digital data will evolve beyond its present form as simple remote communication to become a more sophisticated service.
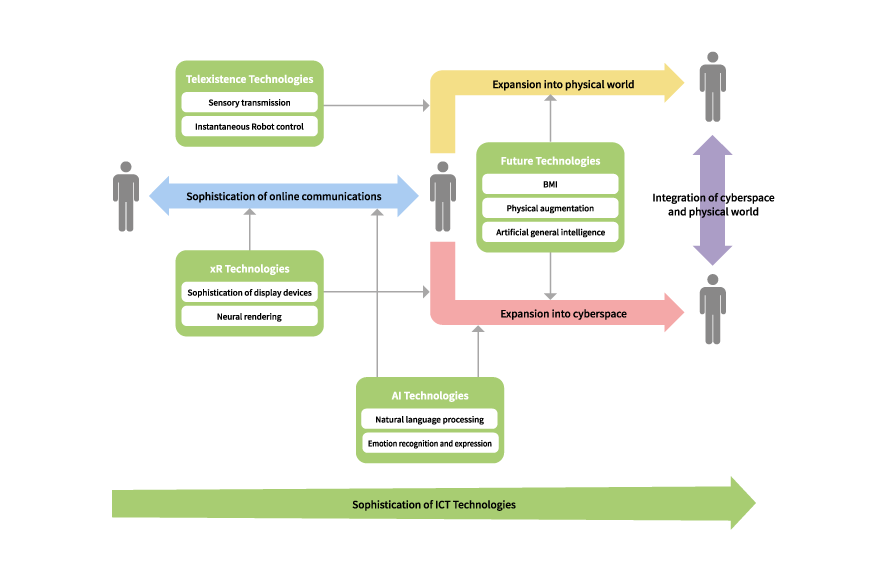
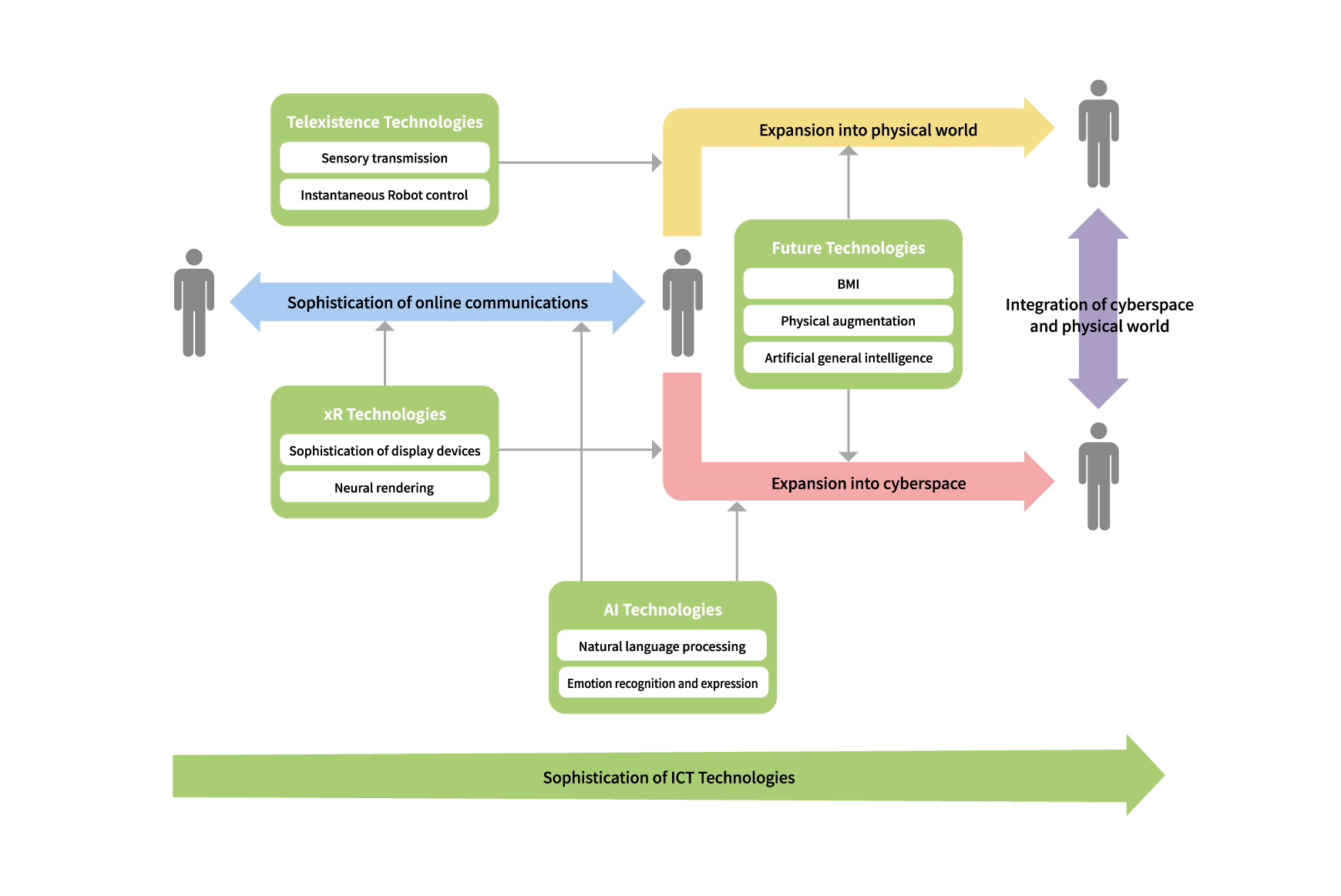
Online communication will no doubt further grow with the progress of ICT such as 5G and edge computing. This article covers four technological areas that will help improve convenience in our daily lives and be applicable to diverse areas: extended reality (xR), artificial intelligence (AI), telexistence, and technologies that will potentially be developed in the future (Figure 1).
In a future world forged through these technologies, an increasing application of ICT, xR, and AI technologies would mean that the scope of online communication would transcend the online framework and expand into cyberspace. Online communication in its current form is the simple conveyance of unaltered, digitized audio and visual data. Online communication can be expanded into the cyberspace by processing digital forms of audio and visual data to facilitate further sharing and mutual understanding of that data by both people and computers. Online communication will enjoy greater value through its expansion into the cyberspace: transcending distance to share not only conversation but experience itself, and even using an avatar to enjoying experiences not possible in reality such as revisiting past experiences.
Concurrently, telexistence technologies will expand online communication to the physical world. Individuals will be able to participate through their own avatar robots in meetings, work, and sightseeing in remote places. A person will be able to simultaneously control multiple avatar robots to perform tasks in parallel.
Through extension into the cyberspace and physical world, online communication is expected to alter use of time and physical distance, gradually transforming the concept of time and space itself. Eventually, this evolution will culminate in the integration of the cyberspace and the physical world online, and the newfound realm will make it possible to support people with physical disabilities or who are frail online— thereby empowering more people to participate in society.
Section two below will provide an overview of xR technologies, the sophistication of display devices, and neural rendering technologies for 3D in the virtual. Section three will examine technologies that will take online communication beyond AI and into the cyberspace such as natural language processing and developments in emotion recognition and expression. Section four dives into telexistence technologies that will take online communication into the physical world such as avatar robot control and transmission of the five senses. Section five will touch on future technologies including those involved in the brain-machine interface (BMI), the augmentation of physical functions and artificial general intelligence, which is a differs from the current, limited forms of AI.
2. xR Technologies
Overview
VR (virtual reality) technology allows users to feel as if they were actually in the virtual world shown on a screen or head mounted display (HMD).
While VR creates an additional virtual space, AR (augmented reality) projects a virtual reality onto the real world, resulting in its augmentation, through the addition of digital information including imagery created by CG.
MR (mixed reality) technology integrates physical and virtual spaces to create a new space where real and virtual objects can interact in real time. The opposite of AR, the virtual world (cyberspace) forms the base on which information from the real world (physical space) is mapped onto the virtual world via a device such as a camera. Since information about the real world can be permanently affixed within the virtual world, multiple people in the same MR space can acquire the same information at the same time and share the same experience.
SR (substitutional reality) technology substitutes and displays a new image in the place of a real-world image. For instance, SR can create the illusion that a past event is once again unfolding before one’s eyes.
xR technologies alter the concept of time and space from a visual perspective. The use of these technologies will help to move online communication beyond mere dialogue and transform it into a means to fulfill multiple purposes and take on a variety forms: from meetings held in a virtual conference room; to work training by remotely superimposing instructions on real images; lectures held in the cyberspace by sharing a large number of videos and CG; and reproduction of battles that took place in old battlefields.
Sophistication of Display Devices
In order to evolve, xR technologies require the sophistication of display devices. Visual input comprises 80 to 90%* of the information that humans receive from the outside world, and vision holds a crucial position in the development of xR technologies.
Currently, HMDs are mainly used as display devices, and no present models can completely reproduce the human field of vision. Humans perceive depth when looking at a solid object by both binocular parallax and monocular focusing. In contrast, HMDs can only reproduce depth by binocular parallax focusing, often resulting in VR sickness.
Various measures are being taken to overcome this issue. One measure involves the development of a technology for projecting an image directly onto the retina instead of placing a display in front of a user’s eyes as with HMDs. Research is underway for a method to recognize space with the naked eye instead of an HMD due to the inevitable facial discomfort experienced when wearing an HMD and the fact that multiple people are not able to share the same experience with the same image. For example, progress has been made on 3D displays, including light field displays, and attempts are being made to reproduce through projection mapping virtual spaces and remote locations.
* Detailed figures vary according to the information source.
Neural Rendering
xR technologies will extend online communication into the cyberspace, and the challenge will shift to the efficient construction of cyberspaces. Currently, 3D computer-generated graphics (CG) requires the creation of 3D models for all the objects involved in advance, and substantial preparation is required to convert any space into 3D CG. Neural rendering is under development as a means to expedite the 3D CD preparation process. Neural rendering uses machine learning to generate 3D CG by extrapolating 3D structure using only information from 2D images.
Advancements in neural rendering will enable the instantaneous construction of virtual worlds in cyberspace at the corresponding location in the real world. Real-world activities will thus become possible to conduct in cyberspace. For example, tourist spots will reproduced in cyberspace, and historical buildings will become visible despite having disappeared in the past. It will become easier to execute simulations that cannot be performed or repeated in the real world.
3.AI Technologies
Overview
The progress of AI technologies has encouraged the practical use of natural language processing and image processing, thus increasing applications in the field of online communication. Although AI is still incapable of understanding language and the outside world in the same way as humans, it is able to generate information that supports and enhances online communication by identifying, extracting, and processing the information that people use in the process.
Natural Language Processing
Progress is being made in the practical application of natural language processing based on AI with regards to input-side processing, such as dialogue comprehension and machine translation, and output-side processing, such as automatic sentence generation.
Machines have long had difficulty in holding natural conversation with humans, and the act of comprehending dialogue, a process on the input side, has been of particular difficulty. However, with technological innovation combining machine learning and corpus-type databases, IBM's Watson AI system left a huge impact in the area of Q&A tasks. Technological progress has since continued in many related fields such as high-precision voice recognition even in the presence of noise. Most recently, AI has seen practical application in making phone reservations on behalf of humans.
In the field of machine translation, deep learning has been successfully utilized in technological innovations resulting in dramatically improved accuracy. DeepL Translator, by the German company DeepL GmbH, was launched in 2017 and is capable of highly accurate and versatile machine translations, even natural translations for Japanese dialects.
On the other hand, automatic sentence generation, a technology on the output side, has seen success with minimum input text. OpenAI, a US non-profit specializing in research on artificial general intelligence, announced in 2020 that its GPT-3 text generation tool could successfully handle a wide range of tasks from just a small amount of data in a process dubbed “small short learning”. The GPT-3 tool has been noted for its high degree of accuracy and will likely see application to a wide range of purposes including the generation of code for computer programs.
The enhancement of natural language processing is expected to significantly reduce communication barriers between people speaking different native languages and those with audiovisual disabilities. AI will reduce human workload, and raise the efficiency and detail of communication through its analysis of the content of received messages and creation of appropriate replies.
Emotion Recognition and Expression
Image processing technology based on AI is presently used for recognizing facial expressions and emotions in online communication and for showing expressions different from conventional ones.
Communication in-person is characterized by the presence of both verbal information and nonverbal cues such as facial expressions, voice tones, and body language. However, users all too often miss this type of information in communication over screens and between avatars. The result is a situation in which participants find it difficult to grasp the subtleties and emotions of other parties. AI-based image processing technology will enable the labeling of facial expressions and emotions on screen.
Practical use has been seen for technologies that read the facial expressions of speakers before reflecting them in avatars. These technologies can overlay additional facial expressions on both the speaker's own image and their character-type avatars.
Conversely, smoother communication has been facilitated through the development of technologies that process a speaker’s facial expressions to either display or hide. Privacy can be protected in online communication by switching a speaker's face to a different one while maintaining their facial expression. Emotions require the use of both facial expressions and voice information for accurate identification. Accordingly, Empath's software makes it possible to quantitatively evaluate and visualize emotional components from voice.
4.Telexistence Technologies
Overview
Telexistence is a technology for augmenting the presence of people to allow them to exist and carryout activities separate from their physical location. Specifically, users can control robots remotely, collectively known as avatar robots. as if they were an extension of the self.
By operating avatar robots as an alter ego, people can carry out activities in remote places, and enjoy freedom from physical disabilities and limitations such as those related to aging and muscle strength. Since multiple avatar robots can be operated simultaneously, multiple tasks can be performed in parallel regardless of travel time or distance. The concept of time and space will change drastically.
The human brain is characterized by its ability to recognize tools that can be operated according to will as body parts. If sensory information can be transmitted to the brain in such a way that tools will move as desired, the new apparatuses will be recognized as a part of the body even if far away. For people to identify with avatar robots as another self, the five senses must be quantified, transmitted, and reproduced and avatar robots must be able carry out actions intended by users in real time.
Sensory Transmission
Current technologies
In the transmission and reproduction of our five senses, vision and hearing are already put into practical use in various fields.
Research is also underway for the transmission and re-creation of haptic information. There are proposals for and emerging examples of technology that quantifies tactile information detected by sensors and categorizes the information as vibration, force, or temperature.
In efforts to quantify and transmit taste information, significant progress has been made in the development of an artificial lipid film type taste sensor that can detect various taste elements such as bitter, sweet, tannic, sour, salty, umami, and rich tastes. Furthermore, prototypes have been made for a device that can reproduce any taste.
On the other hand, smell presents multiple technological challenges postponing practical application due to the many types of odor components that need to be processed, identified, and digitally transmitted in real time and in the same way as the brain does. Nonetheless, various attempts are underway and expected to gradually evolve. Although it still takes time to transmit and reproduce all odors, it is increasingly becoming possible to electronically reproduce odors in remote areas for certain odors.
Cross modal effects
It would be ideal if every piece of information acquired from the outside world through the five senses could be completely transmitted and reproduced. However, this would require the whole body to be enclosed in a special emulation device, far from realistic.
Conveniently, physical values and human perception do not always match. For example, even though it is a ventriloquist who is actually speaking, the audience of such a performance perceives that the dummy itself is speaking due to its mouth movements. Sensations that do not actually exist can be experienced through a combination of past experience with present inputs from the outside world. Such a sensation, created by the interaction of the five senses, is the result of what are known as cross modal effects. The effects both trigger illusions and contributes to highly accurate information transmission. For instance, even if visual information were coarse, it can complement the position of a person or the movement of an object from the direction in which the sound is heard.
Application of cross modal effects are expected to increase in the future as the effects can enhance the sense of reality in online communications without the need to provide all the information of the five senses to humans.
Instantaneous Robot Control: 5G key to real-time control of avatars
To establish the real-time control of avatar robots, there is a need to optimally distribute the control processes among the user’s body, edge servers, and cloud computers. Even more so is the necessity for minimal communication delay between users and their avatars. Fifth generation mobile communication (5G), which started service in 2020, boasts minimal delay in networks overall and is paving the way for practical achievement of the real-time control of avatar robots. Tolerance differs between each of the senses with regard to acceptable levels of delay between actual movement and sensory perception. While visual perception allows for delays of up to 70 ms and auditory tolerances even longer delays, tactile sensation tolerance is as rigid as 1 ms but is feasible with 5G communications.
5.Future Technologies
Overview
New forms of communication will emerge as online communication expands into cyberspace and the physical world. Cyberspace offers freedom from physical and corporeal limitations, and the physical world makes possible for work in remote or dangerous places. Combining the two may produce novel ways of interacting with the real world through cyberspace. Freedom from physical and spatial constraints is expected to be further accelerated with future application of physical augmentation, BMI, and artificial general intelligence technologies.
Physical Augmentation
Avatar robots are the culmination of telexistence technologies, complementing and augmenting functions while maintaining human physicality. The industrial use of avatar robots, capable of moving in conjunction with movement of the human body, has already entered the demonstration phase. Moving forward, it will likely become possible to experience a physical locality through all five senses via avatar robots equipped with sensors. Improvements in maneuverability for avatar robots will enable a natural experience in conducting activities in remote areas through not a screen but all five of the senses—eventually a common feature of daily life. Moreover, if an environment for renting avatar robots from all over the world become a reality, physical travel may become obsolete, especially for business purposes.
Research is also underway on communication unrestricted by human physicality. For example, by equipping drones with input-output mechanisms and HMD-based piloting, users may come to enjoy new points of view in examining both their surroundings as well as themselves. Recent literature asserts that this will provide improved training effects from a third-party perspective and new experiences including out-of-body sensations.
Brain Machine Interface (BMI)
BMI technology measures and analyzes brain activities to control robots. BMI enables users to transmit their behavioral intents directly to robots without any physical input. Identification is possible for brain states and emotions by combining advanced time-series data analysis and data on brain activities such as brain waves and cerebral blood flow. Robots are designed to thus act accordingly.
BMI technologies will play an essential role in bringing to reality communication in the cyberspace without physical movement. Even in the physical space, synergies with physical augmentation technology are progressing, such as research on manipulating a third hand with BMI.
BMI also serves as a predominant technology for input-output mechanisms geared toward those with physical disabilities. Innovation in barrier-free environments may be developed by linking BMI with AI and telexistence technologies.
Meanwhile, research and development on neuroscience is not limited to BMI. For example, optimization of communication may be possible for the medical and mental training fields through the application of brain activity information to the identification of physical and mental health conditions, fatigue levels, and emotions. This could be applied across medical treatment, work support, and learning activities. Neurofeedback offers one example and features the use of resulting information for improving physical conditions while observing brain activities.
Artificial General Intelligence
Artificial general intelligence, once further developed, will ignite improvements in physical augmentation and BMI technologies. Unlike narrow AI, which is tailored to specific issues and usage situations, artificial general intelligence is AI that can act in general situations and features autonomy in such activities. At present, there is no concrete prospects on the development of artificial general intelligence that is completely independent from humans. Nonetheless, AI is gradually becoming more versatile when performing multiple tasks through the combination of various functions and can now be programmed with feelings like curiosity.
The development of artificial general intelligence would mean that avatar robots could be created that work based on intentions and not just simplified instructions. Such a groundbreaking development could result in communication forms that close in on the realization of multiple alter-ego avatars working all over the world in parallel.
Most likely, artificial general intelligence will be used both for operating avatars and supporting the information processing of external inputs. If AI can analyze the input information from sensors and properly transmit them to human beings via the five senses, it may be possible to add extrasensory sensations to AI functions such as seeing colors that were not visible to the eye before or perceiving ultrasonic waves.
6.Conclusion
Increasingly sophisticated thanks to the introduction of new technologies as discussed above, online communication, in addition to changing the concept of time and space, will expand our possibilities and broaden our range of activities. Humanity will enjoy a world free from barriers from language to physical limitations due to disabilities, aging, muscle strength, eyesight, and hearing. Online communication will improve convenience in daily life and enhance the total quality of life by making possible actions that have been made impossible by various forms of existing restrictions.
However, online communication also comes with challenges. It reduces real contact with the outside world and decreases the relative value of the physical body, potentially resulting in changes to human cognitive functions, physical and mental health, and identity formation. In addition, discussion will be vital in the face of changes to social aspects such as culture and ethics.
From the perspective of international competitiveness, Japan's presence in cyberspace is fading relatively, although it is not far inferior to other countries technologically. On the other hand, Japan still commands a strong technical and business presence in the physical world. For the country to maintain its current presence globally, it will need to leverage its strengths in this area. The best strategy would to be the first to develop means to integrate the cyberspace and physical world, thereby securing a leading global position for the country and subsequent opportunities for diverse businesses originating in Japan. To this end, industry, academia, and government must work together and deepen the discussion from both the technological and social perspectives.