Tokyo (July 31, 2023)—Mitsubishi Research Institute, Inc. (MRI) launched a new service that forecasts locational load for electricity. The service is available to electric utilities, with one major provider having already signed on.
MRI helps utilities better align their grid planning with national goals for carbon neutrality while maximizing the use of distributed energy resources (DER)*.
MRI helps utilities better align their grid planning with national goals for carbon neutrality while maximizing the use of distributed energy resources (DER)*.
Source: Mitsubishi Research Institute, Inc.
“Japan’s carbon neutrality can only be achieved by 2050 by making effective use of distributed energy resources such as renewables, battery storage, and electric vehicles,” said Daisuke Miura, project leader at MRI. “Proper grid planning is the key to making this happen. We have been researching, with utilities, how distribution future energy scenarios, or DFES†, should be implemented in Japan, and our new forecasting and support service is based on the findings of that work.”
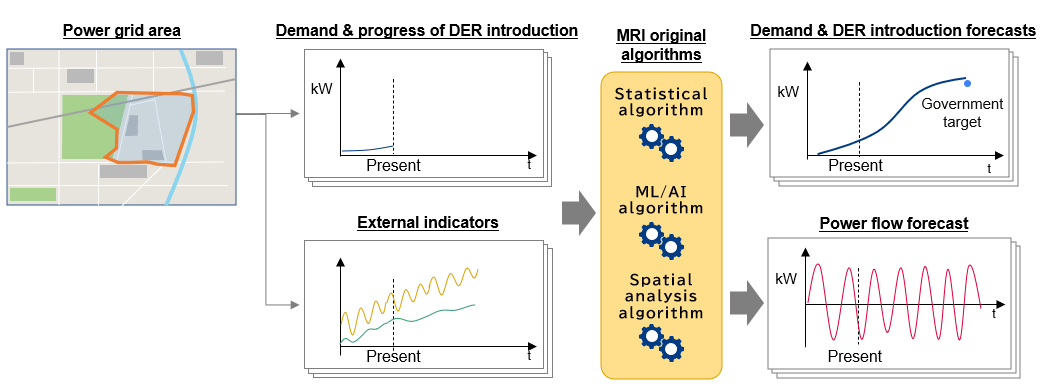
The service uses algorithms developed at MRI to predict electricity demand that reflects unique regional factors. It can forecast both demand growth and future deployment of DERs on a feeder basis, and energy policies, technological trends, economic conditions, and demographic trends are all taken into consideration. The service can also forecast the power flow resulting from DERs installed in the future.
The service uses algorithms developed at MRI to predict electricity demand that reflects unique regional factors. It can forecast both demand growth and future deployment of DERs on a feeder basis, and energy policies, technological trends, economic conditions, and demographic trends are all taken into consideration. The service can also forecast the power flow resulting from DERs installed in the future.
Source: Mitsubishi Research Institute, Inc.
Miura went on to say, “We will contribute to Japan’s goals by supporting the carbon neutrality of utilities across the nation. Our new service will be at the heart of this as we help with the grid planning that carbon neutrality requires. It will also be integral to our wider policy proposals.”
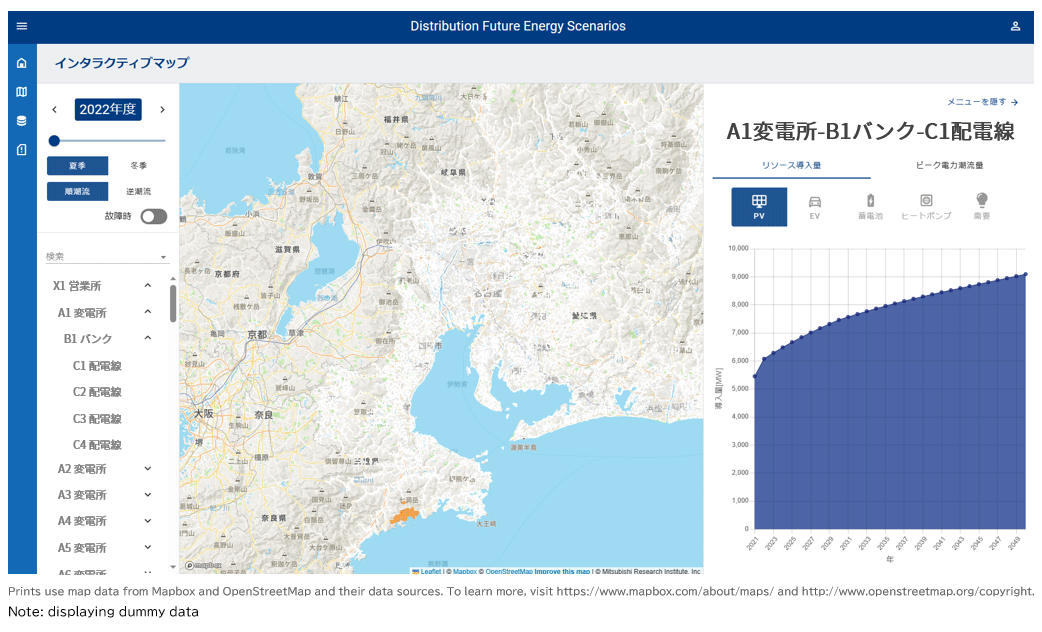
MRI has expanded the service so that it can be used by electric utilities across the country. It features an interface allowing users to create and adjust forecasts themselves, and results can be displayed visually in tables, graphs, and maps.
Future grid planning must accurately reflect the specific situation of each region, such as the spread of DER and the demographic trends. By using information on policy, technology, and regional characteristics to inform forecasts, planners can enjoy better detail and rationality for developing transmission and distribution facilities. This in turn enables the effective use of DERs.
Such regional electricity demand forecasting is already underway in the United Kingdom as DFES. Under the UK’s revenue cap system, electricity distributors must go through the DFES formulation process as a necessary condition for grid planning. Similar systems have been introduced in other countries.
By promoting DFES in Japan, MRI will continue to contribute to Japan's efforts to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050.
MRI has expanded the service so that it can be used by electric utilities across the country. It features an interface allowing users to create and adjust forecasts themselves, and results can be displayed visually in tables, graphs, and maps.
Future grid planning must accurately reflect the specific situation of each region, such as the spread of DER and the demographic trends. By using information on policy, technology, and regional characteristics to inform forecasts, planners can enjoy better detail and rationality for developing transmission and distribution facilities. This in turn enables the effective use of DERs.
Such regional electricity demand forecasting is already underway in the United Kingdom as DFES. Under the UK’s revenue cap system, electricity distributors must go through the DFES formulation process as a necessary condition for grid planning. Similar systems have been introduced in other countries.
By promoting DFES in Japan, MRI will continue to contribute to Japan's efforts to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050.
