
A world where we work, learn, play, relax, and eat with robots every day
How Will Robotics Change Education and Sports in 2030/2040?
Shortage of Teachers an Increasingly Serious Problem in Education
The shortage of teachers in education is a long-standing concern that has yet to be solved. Various media reports clearly portray the extent of exhaustion among teachers. According to the Survey on Teachers' Working Conditions conducted by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) in 2016, a comparison of on-campus daily working hours of employees by job type between 2006 and 2016 showed that working hours increased in 2016 across all job types in both elementary and junior high schools (Figure 1). Moreover, most teachers have many tasks that they have to complete at home and end up working well over 10 hours a day.
On-campus daily working hours of teachers by job type (excluding time of take-home work)
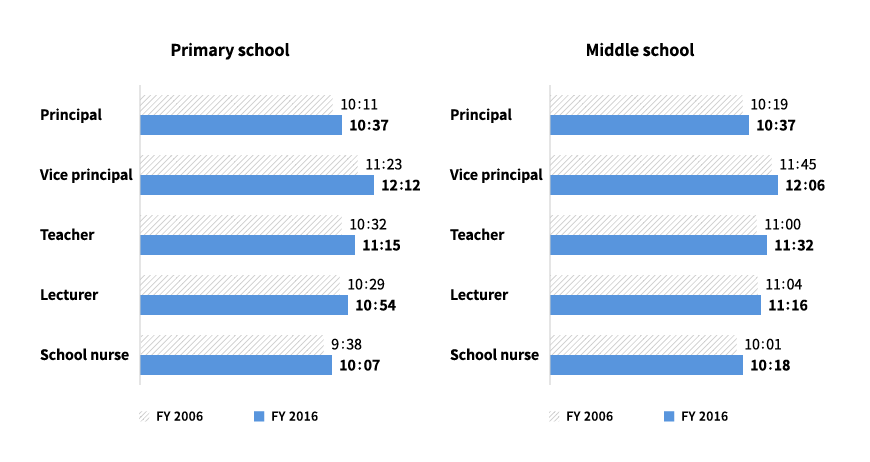
Source: Survey on Teachers’ Working Conditions published by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (FY 2016)
https://www.mext.go.jp/b_menu/shingi/chukyo/chukyo3/079/siryo/__icsFiles/afieldfile/2018/09/28/1409717_4_1.pdf
(Accessed: February 4, 2020)
In addition, according to the “Results of questionnaire related to the situation of securing teachers” (Figure 2) conducted by MEXT in 2018, the reasons for the teacher shortage were the increasing number of teachers taking maternity or childcare leave, the increase in classes for special needs education, the increase in the number of classes due to transfers, the increase in the number of people declining job offers, and the increase in the number of teachers taking sick leave. More than 40% of teachers replied that these reasons were “very true” or “somewhat true.” These results indicate that the number of teachers is insufficient.
Reasons for teacher shortage (related to vacancy or increase in required number of teachers)
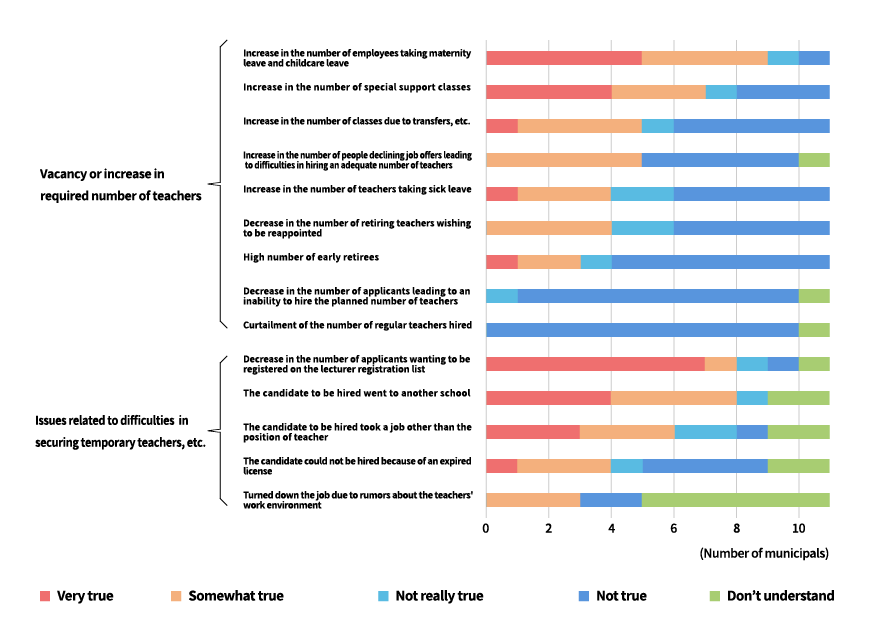
Source: Questionnaire about Teacher Shortage published by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (August 2018)
https://www.mext.go.jp/b_menu/shingi/chukyo/chukyo3/002/siryo/__icsFiles/afieldfile/2018/08/08/1407922_10.pdf
(Accessed: February 4, 2020)
Teachers are required to have skills that were not required until now, such as English and programming. Subjects that teachers must be able to teach are increasing as well. Other challenges are piling up in the area of academia and are too numerous to count, such as regional disparities in education and a decline in the number of opportunities for hands-on learning such as exploring nature and conducting experiments. Even for physical education, there are issues such as the reduced physical strength of children, a lack of coaches, and the development of sports for people with disabilities.
Robots Increasingly Introduced in the Areas of Education and Sports
In order to solve these problems, robots that support teaching are already being used in the education and sports. Let's look at an example.
Education Field
Programming education robots for children and learning support robots that enable active learning are now available. By creating a relaxing atmosphere where the other party is not human, and by using a learning method that involves body movement, these robots elicit positive reactions from children. Robots are used to supplement the teacher shortage, and are beginning to be used in areas where teachers lack expertise, such as programming, and others such as dance education, and language education where practice is essential (Figure 3). In addition, robots are being actively developed for ICT technology such as learning apps, AI teachers, and virtual classrooms.
Example of robot introduction in the education field
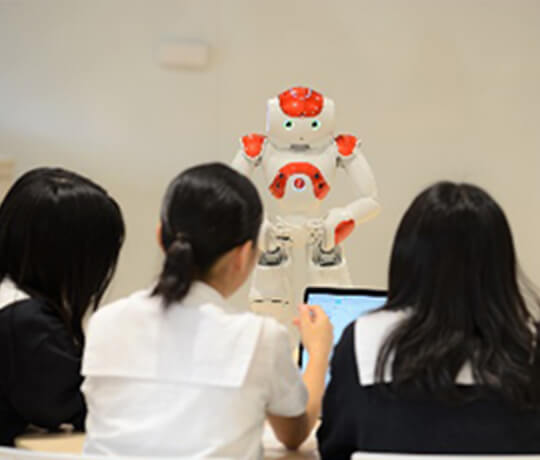

Communication robot NAO developed by SoftBank Robotics (Japan). Through the cultivation of critical thinking skills at elementary, junior high, and high schools, and by using moving robots for programming education, students can experience programming in an easy-to-understand manner and be motivated to learn.
Source: Japan Third Party Co., Ltd.
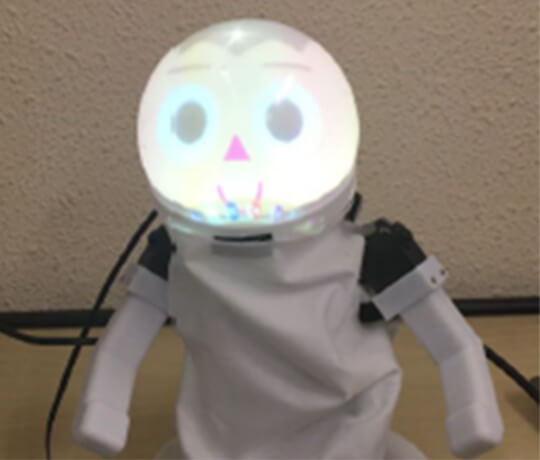

Given that children tend to get bored of learning robotics quickly, Hirotaka Osawa, Assistant Professor at the University of Tsukuba (Japan) conducted a demo experiment where children competed with one another in creating sets of learning materials and operating robots by themselves. His research involves the possibility of active learning using robots.
Source: Hirotaka Osawa, Assistant Professor, University of Tsukuba
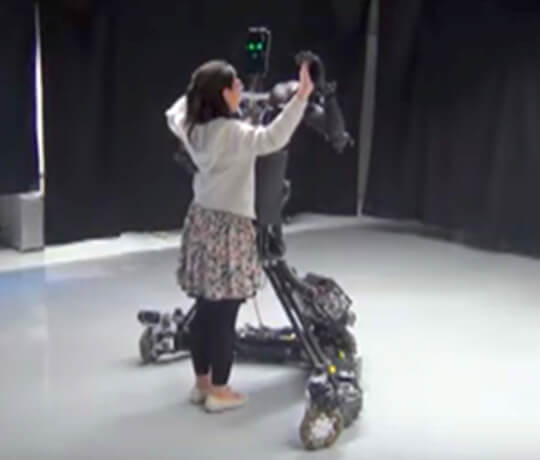

A dance education robot developed by Tohoku University (Japan). It tracks student movements with a force sensor and two laser rangefinders. This is compared with motion capture data that records the movements of a professional dancer to determine if they are dancing well. As the practice progresses, the instructor robot gradually reduces the force it uses to guide the dance.
Source: Video Friday: Robot Dance Teacher, Transformer Drone, and Pneumatic Reel Actuator. June 2, 2017 (IEEE SPECTRUM). https://spectrum.ieee.org/automaton/robotics/robotics-hardware/video-friday-robot-dance-teacher-transformer-drone-pneumatic-reel-actuator
(Accessed: February 7, 2020)
Sports Field
Robots are already used to support top athletes in running, swimming, and other sports by running or swimming with them. In addition, as the necessary gear (equipment) for people with disabilities that participate in sports, robots that correct body movements and robot prosthetic feet that incorporate motors and myoelectric sensors are emerging on the market. There are also various robots presently in the research and demonstration stage such as umpiring AI robots (gymnastics competitions) and soccer balls equipped with sensors. For golf, an autonomous robotic caddy has been developed.
Future Image of Robot Implementation in Education
The practical application of robots in education is expected to continue in the future as a response to the teacher shortage and a means for yielding higher learning effects. Let's take a look at some of the ways in which robots will change education within the next ten to twenty years.
Robots Supporting Teachers
Around 2030, robots that support teachers (avatars) will probably become popular to fill the shortage of teachers with skills in specific fields such as English, mathematics, and programming. These robots will not only teach fixed contents, but will also be equipped with a response function that answers various questions made by students. In addition, with the progress of VR technology, robots used in learning through virtual hands-on experiences such as interacting with nature and learning history, are expected to become practical around 2040.
Virtual hands-on learning robot
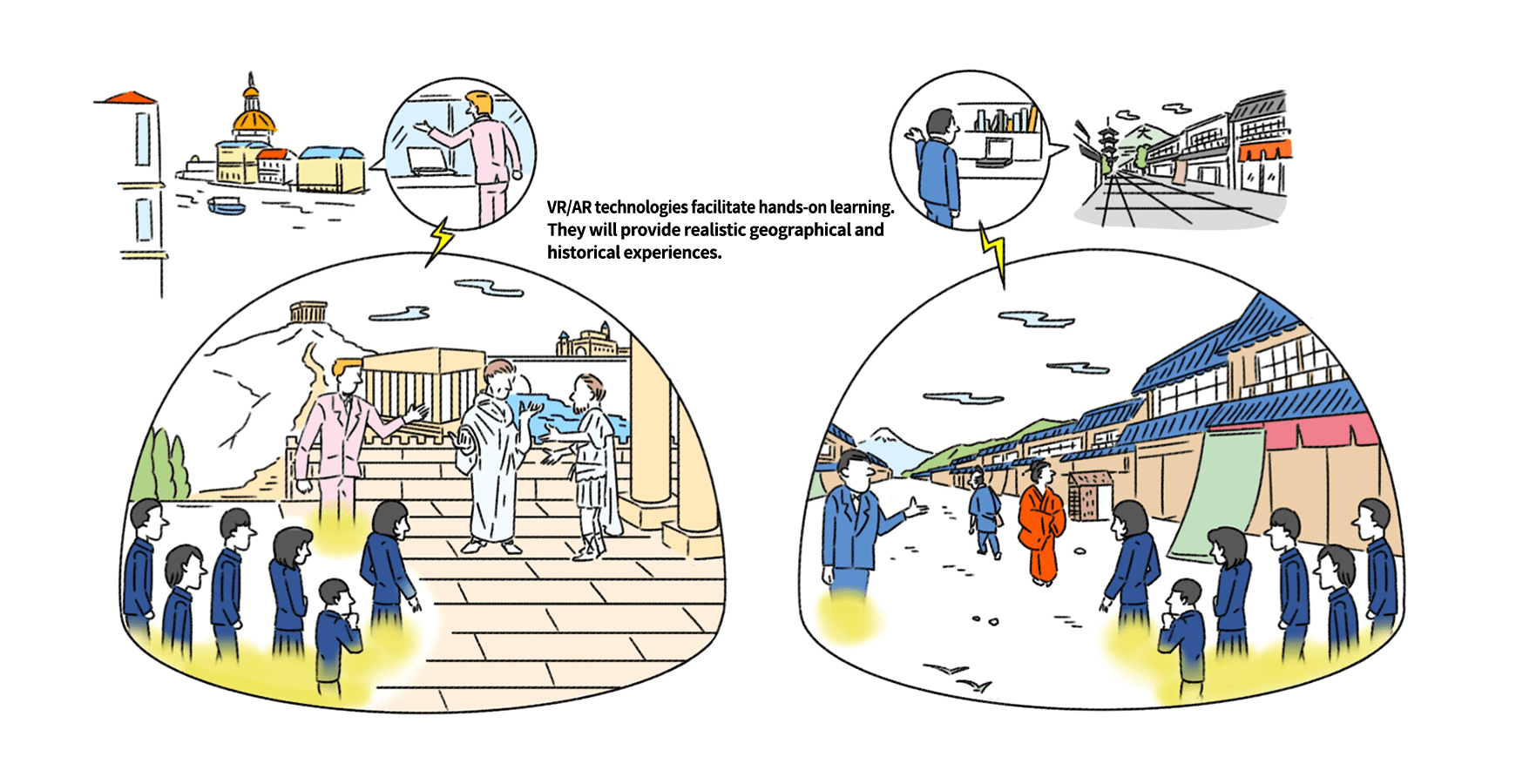
Source: Mitsubishi Research Institute, Inc.
Robots Working in Nurseries and Kindergartens
In nursery schools and kindergartens, robots that play with children and work with nursery teachers are expected to be used from around 2030 in order to respond to the shortage of nursery and kindergarten teachers. (Figure 5).
Robots working in nursery schools and kindergartens
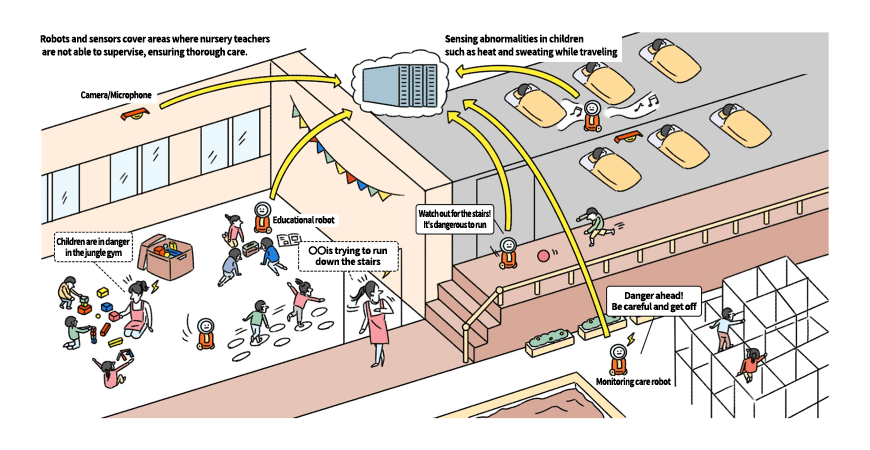
Source: Mitsubishi Research Institute, Inc.
Learning Support Robots Working at Home
Around 2040, learning robots will be introduced into homes, and children will be able to learn various subjects from them. Major cram school (prep school) classes will also start renting robots to provide satellite cram school lessons. These robots not only help children study but also support the lives of children through their various functions. For example, robots capable of multitasking such as waking up or instructing children in the morning are expected to be introduced into the home.
Future Vision of Robot Implementation in Sports
In sports, robots are increasingly being put into practical use for top athletes. This will become more common in the future, and expand into the fields of sports guidance, competition referees, and sports for people with disabilities, further changing competitions themselves. Let’s look at some of the scenarios where robots will be used.
Robots Active in Club Activities and Sports Classes
Around 2040, robots serving as sports instructors are expected to come onto the scene to support running and swimming, and to motivate club members. Pseudo top athlete robots providing simulated experiences on how top athletes move their bodies will also become popular. In addition, robot caddies may be introduced at golf courses, to advise golfers, shout out "Fore!" and find balls.
Robots working in club activities and sports classes
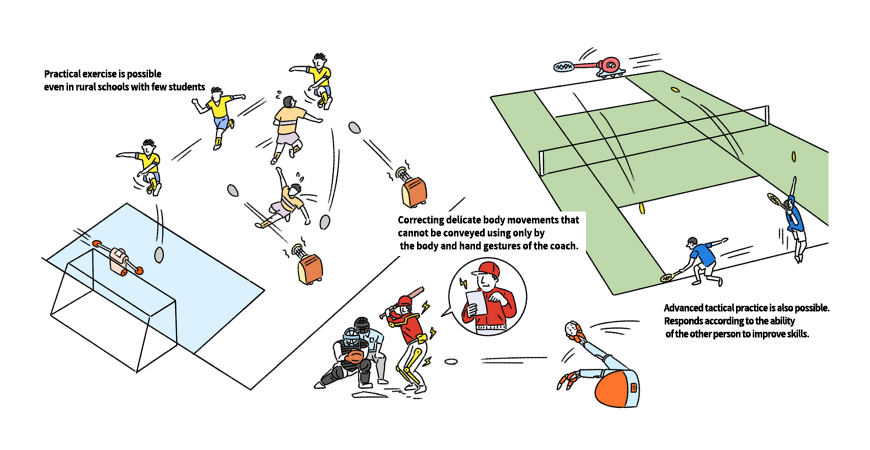
Source: Mitsubishi Research Institute, Inc.
Robots Refereeing in Most Competitions
Around 2030, robot referees will be introduced in scoring competitions such as gymnastics and figure skating to assist referees. By 2040, most referees will be robots. In addition to working as referees in ball games and martial arts, AI robots that can score expression skills will be able to evaluate even artistic skills.
Birth of New Sports for Persons with Disabilities through Robot Support
Historically, sports were the means for people to compete on each other’s strength and have evolved into games like horse racing where humans and horses work together, or bicycle races where athletes use tools to compete on speed. Especially since the beginning of the 20th century, motor sports using automobiles were born. Just as F1 is located at their pinnacle, sports where results are tied to machine performance have become popular.
Around 2040, sports using competitive robots and AI will have become popular. They are expected to have evolved into “universal sports” that allow people of all ages, genders and physiques to compete.
Robot Technology Challenges That Must Be Solved
With the introduction of robots in education and sports, teacher shortages will be resolved and quality improved, expanding the world of new sports. However, there are many challenges that must be overcome to achieve this.
Requirements for Educational Robots with High Qualities
Educational robots will be sought for complex responses, abundant data (knowledge), and accurate answers. To function as coaches, sophisticated listening skills and appropriate responses are required along with subject knowledge. There will be a need to collect a huge amount of data regarding conversations and communication between students and teachers.
Improving ICT Literacy of Teachers Who Can Fully Use Educational Robots (or Alternatives)
School teachers are busy and not familiar with ICT. Even if an ICT company successfully develops an educational robot, the robot may not be used by teachers lacking ICT literacy, thus hindering the introduction of robots. It is therefore imperative to start thinking of ways to improve teachers' literacy or to develop contingency plans that do not depend on literacy.
Expanding the Foundations of Robot Engineers
Robot technology is a collection of various technologies, and new technologies will continue to be added in the future. In Japan, the issue is that the foundations of robot engineers are narrow. In particular, human resources such as engineers who integrate a wide range of elemental and new technologies to build robots or robot technology system producers (RTSPs) are required.
Concerns for Individual Identity Errors Brought about by Human Augmentative Technology
With the advancement of human augmentative technologies, the use of robots and AI to advance human motor functions, the “augmentation” of individual humans will always take place in connected networks even in education and sports. However, when a third party intervenes through the network (for example, through hacking) or when synchronized movements are mistaken for those of an individual, errors may occur.
To protect each individual’s identity, measures are required, such as incorporating a marker function in the system to clearly identify oneself and others (third parties). Such solutions are closely related to technological development in the future. International and governmental organizations will need to impose institutional restraints.
Ensuring Robot Safety
Robots that are close to humans and robots and detect danger such as childcare robots, are related to human safety, life, and death. The issue of legal liability is therefore gradually being raised. To date, the safety of robots that work with humans has been studied and standardized mainly in industrial settings. Moving forward, it will be crucial to urgently consider physical safety and standardization, as robots are used in wider fields.
